What are the 3 Stages of Heat Treatment Process?
Heat treatment is a process of heating and cooling metal materials to achieve desired mechanical properties, such as hardness, toughness, and ductility. This process involves three main stages: heating, soaking, and cooling. In this article, we will discuss each stage of the heat treatment process and the role of the heat treatment furnace in achieving the desired results.
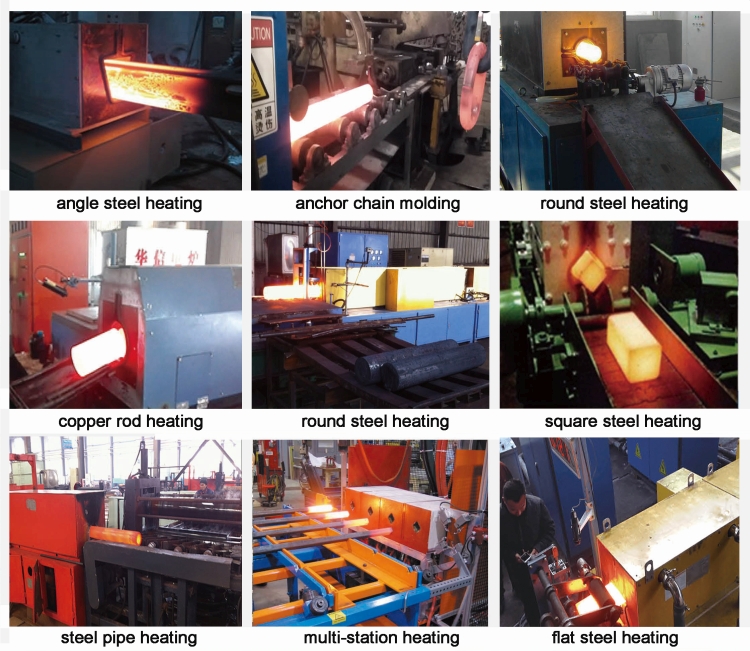
Stage 1: Heating
The first stage of the heat treatment process is heating. The metal material is placed in a furnace and heated to a specific temperature, depending on the type of material and the desired outcome. The heat treatment furnace is designed to provide a controlled environment for the metal to reach the desired temperature without being exposed to oxygen and other contaminants.
During the heating stage, the metal undergoes a process called annealing. This is where the metal is heated to a temperature that allows the atoms to move more freely, resulting in a reduction of internal stresses and an increase in ductility. Once the annealing process is complete, the metal is ready for the next stage.
Stage 2: Soaking
The second stage of the heat treatment process is soaking. During this stage, the metal is held at a specific temperature for a set amount of time to ensure that the heat is evenly distributed throughout the material. This is important because it allows the metal to reach a uniform temperature, which is necessary for achieving the desired mechanical properties.
The heat treatment furnace is designed to maintain a consistent temperature during the soaking stage. This ensures that the metal is heated evenly and that the desired mechanical properties are achieved.
Stage 3: Cooling
The final stage of the heat treatment process is cooling. Once the metal has been heated and soaked, it is cooled at a controlled rate to achieve the desired mechanical properties. The cooling rate is critical because it determines the final properties of the metal. The heat treatment furnace is designed to provide a controlled cooling environment to achieve the desired results.
There are two common cooling methods used in heat treatment: quenching and tempering. Quenching involves rapidly cooling the metal in a liquid, such as water or oil, to achieve a high level of hardness. Tempering involves slowly cooling the metal to achieve a balance of hardness and toughness.
In conclusion, the heat treatment process involves three main stages: heating, soaking, and cooling. The heat treatment furnace plays a critical role in providing a controlled environment for the metal to achieve the desired mechanical properties. By understanding the stages of the heat treatment process, manufacturers can produce metal materials with the desired properties for their specific applications.

